Google indexing issues can significantly affect your website’s visibility and performance in search engine results. Understanding how to manage these issues is crucial for any website owner or digital marketer. This guide will walk you through the process of adding your website to Google Search Console, indexing content, identifying common indexing problems, sitemap, and implementing effective solutions.
How to Add a Website Property to Search Console for Indexing Purposes
To begin addressing indexing issues, you must first add your website to Google Search Console (GSC). This tool provides valuable insights into how your site is performing in Google searches. Here’s how to add a property:
Go to the Google Search Console homepage: Start by navigating to the GSC homepage.
Click Start Now: Sign in with your Google account.
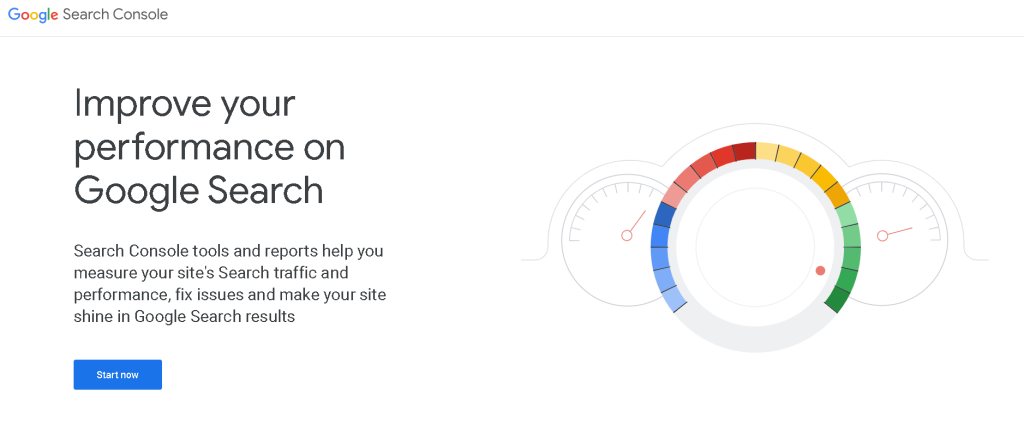
Enter your website’s URL and click Add Property: You can choose between a domain property (which covers all subdomains) or a URL prefix property (which is specific to a certain URL).
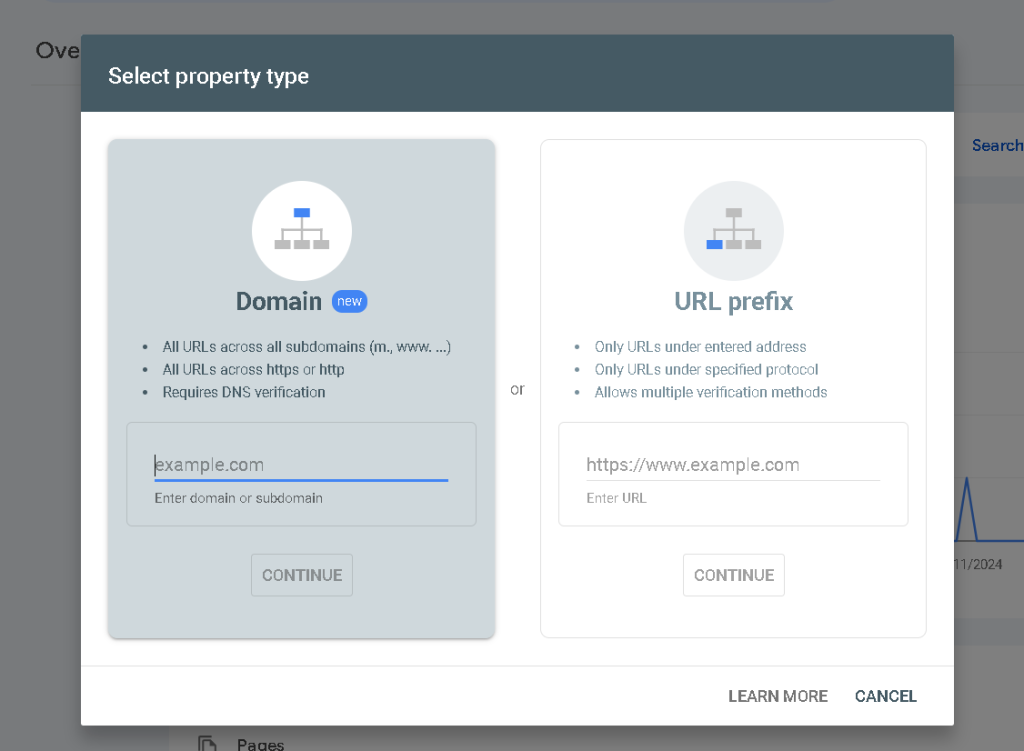
Verify ownership of your website: Verification can be done through various methods, including adding an HTML tag to your site, uploading an HTML file, or using Google Analytics.
To submit a URL for indexing, you can:
Select a Property: Choose the property you just added.
Copy the URL you want to submit: Ensure it is the exact URL you wish to index.
Paste the URL into the URL Inspection tool: This tool will check if Google can access and index your page.
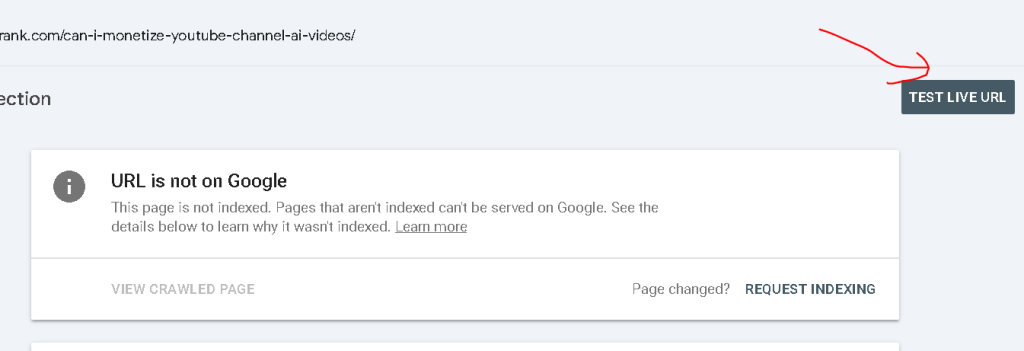
Click Test Live URL to check if the URL is index-able: This will show any potential issues that may prevent indexing.
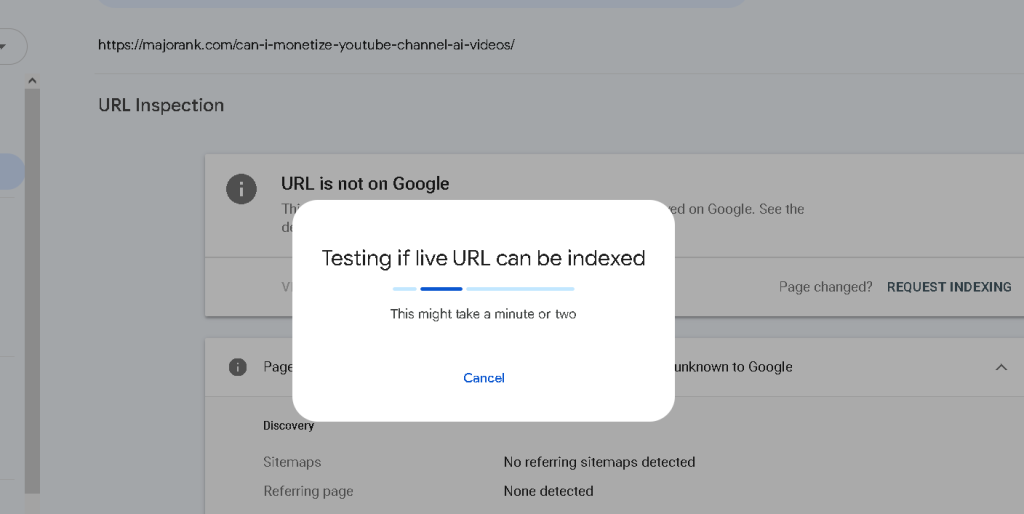
Click Request Indexing: If everything checks out, request that Google index this URL.
By following these steps, you ensure that your website is properly set up for indexing and can be monitored for any issues.
Common Google Indexing Issues
Several factors can hinder Google’s ability to index your site effectively:
- Website Is Too New: New websites may take time before they are indexed due to lack of authority and backlinks.
- No Domain Name: Sites without a registered domain name cannot be indexed.
- Recent Web Redesign: Significant changes may lead Google to reevaluate how it indexes your site.
- Missing Sitemap: A sitemap helps search engines understand your site’s structure; without it, indexing may be inefficient.
- Poor Site Structure: Complicated navigation can confuse crawlers and hinder indexing.
- Orphan Pages: Pages without internal links are hard for crawlers to find and index.
- Not Mobile-Friendly: With mobile-first indexing, sites not optimized for mobile may struggle with visibility.
- Not ADA Compliant: Accessibility issues can affect user experience and indexing indirectly.
- Low-Quality Content: Thin or duplicate content may be ignored by Google’s algorithms.
- Noindex Tag or Header Is Blocking Googlebot: Incorrect settings can prevent pages from being indexed.
- Redirect Loops: These create confusion for crawlers, preventing them from reaching content.
- Exceeded Crawl Budget: Large sites may exceed their crawl budget if not optimized properly.
- Suspicious or Hard-to-Read Code: Poor coding practices can impede crawling and indexing efforts.
- Incorrect Canonical Tags: Misconfigured canonical tags can lead Google to index the wrong versions of pages.
- Received a Google Penalty: Penalties can drastically affect how and if pages are indexed.
Understanding these issues is key in diagnosing why certain pages might not be appearing in search results.
Also Read About – What are the success factors of SEO
How to Fix Google Indexing Issues?
To resolve common indexing issues, consider these tailored solutions:
- For new websites, focus on building backlinks and increasing authority through quality content and social media engagement.
- Ensure that your domain name is registered and active; without it, there’s no chance of being indexed.
- After redesigning your site, submit an updated sitemap and monitor changes through GSC.
- Create and maintain an XML sitemap that lists all important pages on your site; submit this via GSC regularly.
- Optimize your site structure with clear navigation paths and internal linking strategies to help crawlers discover all pages easily.
- Link orphan pages from other relevant content within your site so they become discoverable by crawlers.
- Ensure mobile-friendliness by using responsive design techniques; test using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
- Review accessibility guidelines (ADA compliance) and make necessary adjustments for better user experience and SEO benefits.
- Invest time in creating high-quality content that provides value; avoid duplicate content issues by consolidating similar pages with canonical tags where necessary.
- Regularly audit your site for technical SEO issues like redirect loops or crawl budget management; tools like Screaming Frog can help identify these problems.
- Check canonical tags for accuracy; ensure they point correctly to preferred versions of pages without conflicts.
By systematically addressing these issues, you can significantly improve your site’s visibility in search results.
What is a Sitemap?
A sitemap is essentially a roadmap of your website that helps search engines navigate its structure more effectively. It lists all important URLs on your site along with additional metadata about each page (like when it was last updated). Sitemaps come in two main types:
- XML Sitemaps: Designed specifically for search engines; they help bots understand which pages are important and should be crawled first.
- HTML Sitemaps: Created for users; they provide a user-friendly overview of site navigation.
For example, an XML sitemap might look like this:
This format allows search engines like Google to efficiently crawl and index the listed URLs.
How to Submit a Sitemap
Submitting a sitemap helps ensure that all critical pages on your site are indexed promptly. Here’s how you can submit one:
- From Your Website Backend:
- Generate an XML sitemap using plugins if you’re on platforms like WordPress (e.g., Yoast SEO).
- Save the sitemap file (usually named
sitemap.xml) in the root directory of your website.
- Using SEO Tools Like Yoast:
- If using Yoast SEO, navigate to SEO > General > Features tab within WordPress dashboard settings. Ensure that “XML sitemaps” is enabled.
- To Submit Your Sitemap in Google Search Console:
- Log into GSC and select the property associated with your website.
- In the left-hand menu, click on “Sitemaps.”
- Enter the URL of your sitemap (e.g.,
https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml) in the provided field and click “Submit.” - After submission, monitor its status under “Sitemaps” in GSC for any errors or processing messages.
By following these steps diligently, you enhance not only indexing but also overall SEO performance for better visibility on search engines.
FINAL THOUGHT
In conclusion, managing Google indexing issues involves understanding both technical aspects of SEO as well as strategic content creation. By utilizing tools like Google Search Console effectively and addressing common pitfalls proactively, you position your website for success in search rankings.
Citations:
[1] https://www.bluehillsdigital.com/articles/google-search-console-add-verify-website/
[2] https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/7687465?hl=en
[3] https://support.hostinger.com/en/articles/6511296-website-builder-how-to-verify-a-url-property-at-google-search-console
[4] https://sitekit.withgoogle.com/documentation/using-site-kit/choosing-a-search-console-property/
[5] https://www.shopify.com/ng/blog/google-search-console
[6] https://learn.showit.com/en/articles/6150129-add-property-to-google-search-console
[7] https://www.semrush.com/blog/google-search-console/
[8] https://search.google.com/search-console/about